Abstract
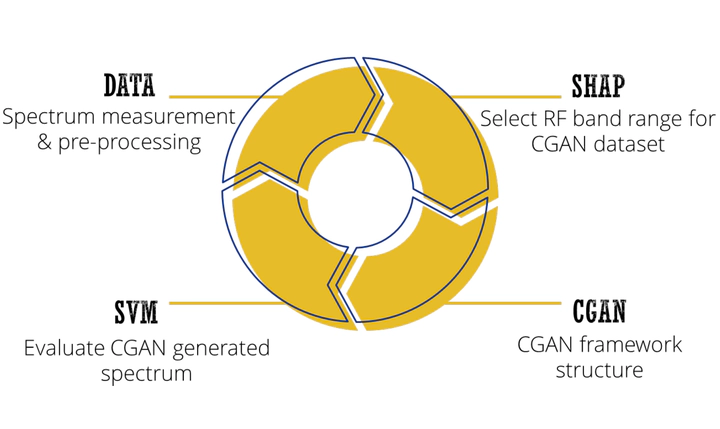
This paper proposes an innovative machine-learning-based method to extract compact, accurate, and adequate human radio frequency signature in residential environment. Our research created a shielded environment by using electromagnetic fields blocking material to attenuate strong signals in the background. SHapley Additive exPlanations were utilized to identify the most human impacted frequency range, which ensures the spectrums acquired later contain adequate information. In order to extract the spectrum that contains mainly human signature information, a conditional-generative-adversarial network has been trained to model the shielding effect. The proposed method can generate the spectrum containing the human signature that was originally buried in the background. In addition to simulating the denoising effect that is established by the physical shielding, the trained generator model is applied for the second time to achieve multi-stage denoising, which further improves the signal to noise ratio in the spectrum. As the result shown, the proposed model successfully generates the spectrum with root mean square distance of 0.027 when comparing with the physically shielded spectrum. Furthermore, a Support Vector Machine model is trained to evaluate the performance of the conditional generative adversarial network model. The experimental results show that the extracted human signature in the synthesized spectrum can be identified by the support vector machine classifier with 100% accuracy while the physically shielded spectrum yields 93.5% accuracy.